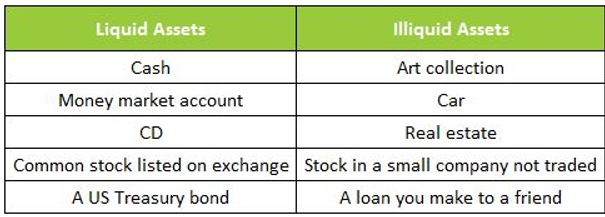
In the world of personal finance, liquidity plays a crucial role in ensuring financial stability and security. Liquidity refers to the ability to convert assets into cash quickly without significant loss in value. It is an important concept to understand as it affects various aspects of our financial lives. In this article, we will explore different subtopics related to liquidity and how they impact our personal finances.
Illiquid assets are those that cannot be easily converted into cash without substantial time or cost. Examples include real estate, art collections, and private equity investments. Investing in illiquid assets can offer higher potential returns but comes with the risk of limited access to funds when needed. It’s important to carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks before allocating a significant portion of your portfolio towards illiquid assets.
Liquidity risk management involves assessing and managing the potential risks associated with insufficient liquidity. This includes having a contingency plan in place for unexpected events such as job loss or medical emergencies that may require immediate access to funds. By maintaining a well-diversified portfolio with a mix of liquid and illiquid assets, along with an emergency fund, you can mitigate liquidity risks.
Cash equivalents are highly liquid investments that can be easily converted into cash within a short period, typically less than three months. These include treasury bills, money market instruments, and certificates of deposit (CDs). Cash equivalents provide stability and easy access to funds while still generating some level of return.
Money market funds are mutual funds that invest in low-risk short-term debt securities like government bonds and commercial paper. They aim to maintain stable net asset values (NAV) per share by investing in highly liquid securities. Money market funds provide individuals with an opportunity to earn interest on their excess cash while maintaining high levels of liquidity.
Emergency funds act as a safety net during unforeseen circumstances such as job loss or unexpected expenses like medical bills or car repairs. These funds should ideally cover three to six months’ worth of living expenses and be easily accessible in a liquid form. By having an emergency fund, you can avoid dipping into long-term investments or going into debt during challenging times.
Liquidation value refers to the estimated worth of an asset if it were sold quickly, typically at a discount to its fair market value. It is commonly used when valuing distressed assets or companies facing financial difficulties. Understanding the liquidation value of your assets can provide insight into their potential worth in worst-case scenarios.
Liquidity ratios are financial metrics that assess a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations using its current assets. The most common liquidity ratios are the current ratio and quick ratio (also known as acid-test ratio). These ratios help investors and analysts evaluate a company’s liquidity position before making investment decisions.
The liquidity preference theory is an economic concept that suggests individuals have a higher preference for holding money in highly liquid forms rather than investing it due to uncertainty and risk aversion. This theory explains why people demand higher returns on investment options with less liquidity.
In contrast, a liquidity trap occurs when interest rates are already low, but consumers and businesses still hoard cash instead of spending or investing it. In such situations, monetary policy becomes less effective because lowering interest rates further may not stimulate economic growth or encourage borrowing.
Market liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without causing significant price fluctuations, while funding liquidity relates to access to short-term funding sources for banks and financial institutions. Both types of liquidity are crucial for maintaining stable markets and ensuring smooth functioning of the financial system.
These concepts also extend beyond personal finance as they impact various sectors such as banking and investment management. For example, intraday liquidity management focuses on monitoring and managing cash flows throughout the day within banks to ensure sufficient funds are available at all times.
Regulations like Basel III aim to enhance banking system stability by introducing stringent requirements related to capital adequacy, leverage ratios, and liquidity. Liquidity stress testing is another tool used by regulators to assess a financial institution’s ability to withstand adverse economic conditions.
In conclusion, understanding liquidity and its subtopics is essential for individuals seeking to achieve financial security. By managing illiquid assets, implementing effective risk management strategies, and maintaining emergency funds, we can navigate unexpected situations with ease. Additionally, knowledge of various liquidity concepts helps us make informed investment decisions and be aware of potential risks in the financial marketplace.