Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is a popular investment strategy that involves regularly investing a fixed amount of money into a particular asset or securities over an extended period. This approach aims to mitigate the impact of market volatility and reduce the risk associated with trying to time the market.
The concept behind dollar-cost averaging is relatively straightforward. Instead of attempting to predict whether the market will go up or down, investors commit to investing a predetermined amount at regular intervals, such as monthly or quarterly. By doing so, they buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when prices are high, effectively reducing the average purchase price per share over time.
How Dollar-Cost Averaging Works
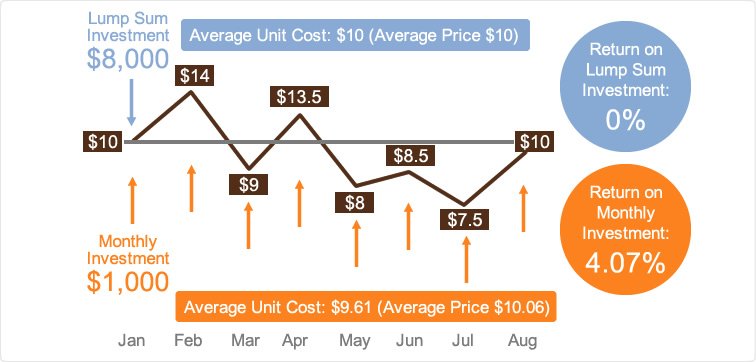
To understand how dollar-cost averaging works in practice, let’s consider an example. Suppose you have $1,000 that you want to invest in Company XYZ’s stock. Instead of buying all $1,000 worth of shares at once, you decide to spread out your investments over ten months by investing $100 each month.
In Month 1, Company XYZ’s stock is trading at $10 per share; therefore, you purchase 10 shares ($100/$10). In Month 2, the stock price drops to $8 per share. You can now afford to buy 12.5 shares ($100/$8).
Month after month, regardless of whether the stock price goes up or down, you continue purchasing shares using your fixed investment amount until all your funds have been invested.
Over time, this approach safeguards against making large investments during periods when prices are high while taking advantage of lower prices during market downturns.
Benefits of Dollar-Cost Averaging
One significant benefit of DCA is its ability to minimize emotional decision-making driven by short-term market fluctuations. It encourages discipline by eliminating impulsive reactions based on fear or greed that may lead investors astray from their long-term goals.
Additionally, dollar-cost averaging reduces exposure to timing risks. Attempting to time the market accurately is challenging even for seasoned investors. By investing regularly, regardless of market conditions, you avoid the pressure of making precise predictions about when to buy or sell.
DCA can also help in managing risk. Since you invest a fixed amount on a regular schedule, you reduce the impact of sudden market downturns. If prices drop significantly during one period, your investment buys more shares at lower prices, potentially increasing future returns as markets recover.
Another advantage of DCA lies in its suitability for investors with limited funds. Rather than needing a large sum upfront to invest all at once, individuals can start small and gradually build their portfolio over time.
Potential Drawbacks
While dollar-cost averaging offers several advantages, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks too.
Firstly, this strategy assumes that the asset being invested in will increase in value over time. While historical data suggests that stock markets tend to rise over extended periods, there are no guarantees. Investors should assess the long-term prospects and risks associated with the investment before implementing DCA.
Secondly, while DCA helps mitigate downside risk during falling markets by buying more shares at lower prices, it also limits upside potential during rising markets since fewer shares are purchased at higher prices. This means that if an investment performs exceptionally well over a specific period, DCA may result in missing out on maximizing profits compared to investing a lump sum initially.
Choosing Investments for Dollar-Cost Averaging
When selecting investments for DCA, it’s crucial to consider factors such as diversification and risk tolerance.
Diversification involves spreading your investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds), sectors (technology, healthcare), or geographic regions (domestic vs international). By diversifying your portfolio through multiple investments rather than concentrating on one particular security or company’s stock price movement alone reduces overall risk exposure.
Risk tolerance refers to an individual investor’s ability and willingness to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. It is vital to assess your risk tolerance before selecting securities for DCA.
For example, if you have a high risk tolerance and are investing for long-term growth, you might choose to allocate a higher percentage of your funds towards stocks. On the other hand, if stability and income generation are more important, bonds or other fixed-income instruments might be more suitable.
Implementing Dollar-Cost Averaging
To implement dollar-cost averaging effectively, it’s essential to follow a few key steps:
1. Determine Your Investment Objectives: Clarify your investment goals and time horizon. Are you investing for retirement? Saving for a down payment on a house? Knowing your objectives will help guide your investment decisions.
2. Set an Investment Schedule: Decide on the frequency of your investments (monthly, quarterly) and the amount you’re comfortable committing each time.
3. Choose Suitable Investments: Select assets that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance level.
4. Automate Your Investments: To ensure consistent contributions, set up automatic transfers from your bank account to your chosen investment account(s).
5. Regularly Review Your Portfolio: Periodically review the performance of your investments and make adjustments based on changes in market conditions or personal circumstances.
Conclusion
Dollar-cost averaging is an effective strategy that can help investors navigate market volatility while reducing emotional decision-making biases associated with timing the market perfectly. By consistently investing predetermined amounts over time, this approach allows individuals to build wealth gradually while minimizing downside risks.