Tax season can be a stressful time for many individuals, but understanding the various tax implications and deductions can help ease some of that burden. In this article, we will delve into 25 important tax topics that individuals should be aware of when it comes to their personal finances.
1. Tax deductions for medical expenses: Medical expenses can add up quickly, but luckily there are certain deductions available. Individuals may be able to deduct qualified medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of their adjusted gross income (AGI). This includes costs such as doctor visits, prescription medications, and health insurance premiums.
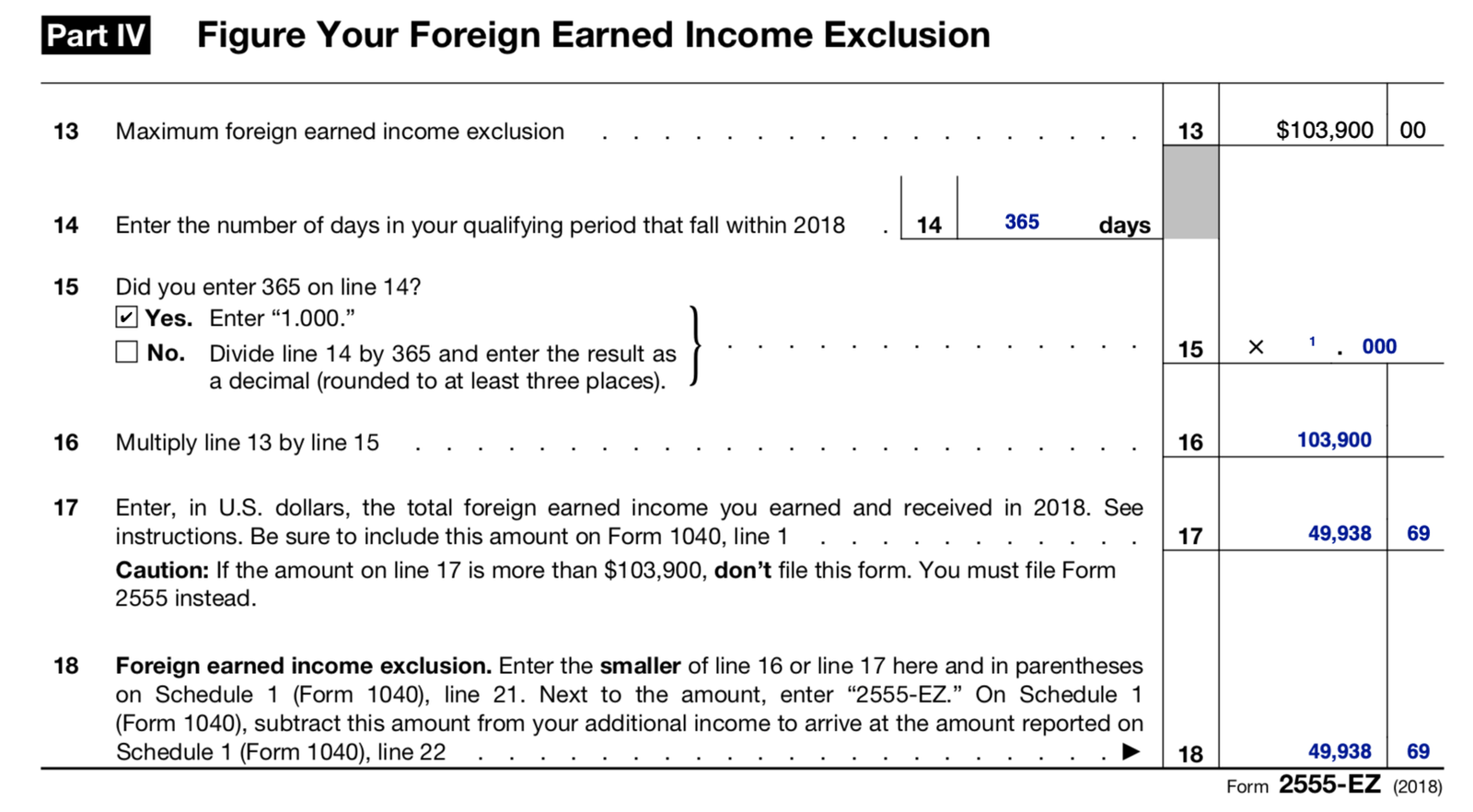
2. Exclusion of foreign earned income: If you work overseas and meet certain requirements, you may qualify for an exclusion on your foreign earned income up to a specific limit set by the IRS. This exclusion helps alleviate double taxation for those living and working abroad.
3. Reporting self-employment income: If you’re self-employed or own a small business, it’s crucial to accurately report your income on your tax return. Self-employment taxes must be paid in addition to regular income taxes, so keeping detailed records is essential for proper reporting.
4. Treatment of capital gains and losses: Capital gains refer to profits made from selling investments like stocks or real estate, while capital losses occur when these assets are sold at a loss. The tax treatment varies depending on whether they are short-term (held less than one year) or long-term (held more than one year), with different rates applied accordingly.
5. Deductible contributions to retirement accounts: Contributing money to retirement accounts like traditional IRAs or 401(k)s not only helps secure your financial future but also offers potential tax advantages in the present day. These contributions are often deductible from taxable income within certain limits set by the IRS.
6.Taxable Social Security benefits: Depending on an individual’s overall income level during retirement, some portion of their Social Security benefits may become taxable. The specific rules for calculating the taxable amount can be quite complex, so consulting a tax professional is recommended.
7. Education-related tax credits and deductions: Higher education can be expensive, but there are various tax credits and deductions available to help offset these costs. Examples include the American Opportunity Credit, Lifetime Learning Credit, and deductions for qualified tuition and fees.
8. Alimony payments and their impact on AGI: If you pay alimony to an ex-spouse as part of a divorce agreement finalized before 2019, these payments may be deductible from your AGI. Conversely, if you receive alimony payments, they must be included as income on your tax return.
9.Tax implications of rental property income: Rental property owners should understand the tax implications of their investment. Income generated from rent is typically considered taxable, while expenses related to managing the property may be deductible against that income.
10.Reporting gambling winnings and losses: Gambling winnings are generally considered taxable income and must be reported on your tax return. However, it’s important to note that you can also deduct gambling losses up to the amount of your winnings if you itemize deductions.
11.Treatment of unemployment compensation for tax purposes: Unemployment benefits received during periods of joblessness are considered taxable income by the federal government. It’s crucial to report these benefits accurately when filing your taxes.
12.Deductible student loan interest: If you have been repaying student loans throughout the year, there is potential relief in terms of deducting the interest paid on those loans from your AGI – subject to certain limitations set by the IRS.
13.Impact of moving expenses on AGI: In most cases since 2018 under current law changes (unless in military), moving expenses incurred due to work relocation are no longer deductible unless eligible under special circumstances like members of Armed Forces or National Guard who move pursuant to certain military orders concerning permanent change-of-station moves.
14.Deductible business expenses for self-employed individuals: As a self-employed individual, you can deduct various business-related expenses to reduce your taxable income. These may include office supplies, travel expenses, and even a portion of your home’s utility bills if you have a dedicated office space.
15.Tax consequences of receiving an inheritance or gift: Generally, inheritances are not subject to federal income tax. However, any income generated by inherited assets after receiving them may be taxable. Gifts received from others are also generally not taxable as income but might have other reporting requirements depending on the size and type of gift.
16.Reporting rental property depreciation on taxes: Depreciation is an accounting method that spreads out the cost of a rental property over its useful life. This expense can be deducted each year and helps offset the rental income for tax purposes.
17.Deductions for home office expenses: If you use part of your home exclusively for business purposes, you may qualify for deductions related to home office expenses such as utilities, insurance, and maintenance costs. The IRS has specific rules regarding what qualifies as a deductible home office expense.
18.Tax treatment of alimony received: Alimony payments received are considered taxable income and must be reported on your tax return in most cases unless modified by certain agreements finalized before 2019 or under special circumstances like separate taxation when divorced spouses live apart throughout the year.
19.Impact of health savings accounts (HSAs) on AGI: Contributions made to HSAs offer potential tax advantages since they are typically deductible from your AGI. Additionally, withdrawals used for qualified medical expenses are often tax-free.
20.Deductions for charitable contributions: Donating money or goods to qualifying charitable organizations can result in valuable deductions that lower your overall tax liability. It’s important to keep proper documentation and follow IRS guidelines when claiming these deductions.
21.Reporting income from freelance work or gig economy jobs: Income earned through freelance work or gig economy jobs is generally taxable and must be reported on your tax return. Keep track of all income received and related expenses to ensure accurate reporting.
22.Treatment of state and local taxes paid: Many individuals can deduct the amount they paid in state and local taxes from their federal tax liability, subject to certain limitations set by the IRS. This deduction helps alleviate the burden of paying taxes at multiple levels.
23.Tax implications of early withdrawals from retirement accounts: Withdrawing money from retirement accounts before reaching a certain age typically incurs penalties and additional taxes. It’s important to understand these consequences before making early withdrawals.
24.Impact of investment losses on AGI: Capital losses incurred when selling investments can help offset capital gains for tax purposes. If your capital losses exceed your gains, you may be able to deduct up to $3,000 against other types of income, with any remaining loss carried over to future years.
25.Deductible mortgage interest payments: For many homeowners, mortgage interest payments are deductible from their AGI if they itemize deductions instead of claiming the standard deduction. This deduction can provide significant savings for those with large mortgages or high-interest rates.
While this article provides an overview of various tax topics that individuals should be aware of, it’s essential to consult with a qualified tax professional or utilize reliable software when preparing your own personal income tax return. Tax laws are complex and subject to change, so staying informed is crucial for maximizing deductions and minimizing potential errors on your return.